Carroll izard says that love – In the realm of emotions, Carroll Izard’s groundbreaking theory has shed light on the intricate nature of love. Embark on a journey to explore his insights, uncovering the diverse expressions of love and its profound impact on our lives.
Izard’s research has illuminated the multi-faceted nature of love, revealing its intricate interplay with our emotions and shaping our relationships. This article delves into his theory, examining the emotions that intertwine within love and their manifestations in our lives.
Carroll Izard’s Theory of Emotion

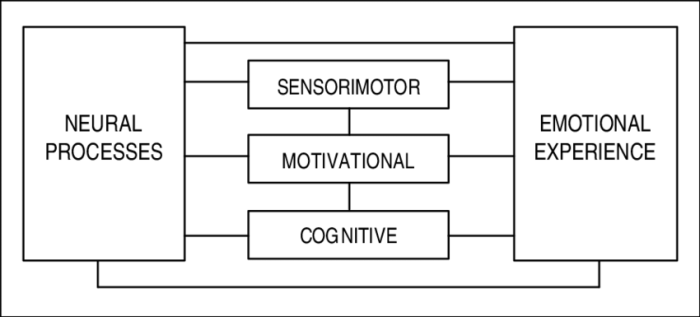
Carroll Izard’s theory of emotion is a prominent theory in the field of psychology that focuses on the relationship between emotions and facial expressions. Izard proposed that there are ten basic emotions that are universally expressed across cultures and that these emotions are associated with specific facial expressions.
Basic Principles of Izard’s Theory
Izard’s theory is based on the following principles:
- Emotions are innate and biological, not learned or acquired.
- Emotions are organized into a hierarchical structure, with some emotions being more basic than others.
- Emotions are expressed through facial expressions, which are universal across cultures.
- Facial expressions are not simply reflexes but are instead controlled by the brain.
- Emotions can be triggered by both internal and external stimuli.
Izard’s Ten Basic Emotions
Izard identified ten basic emotions that he believed were universally expressed across cultures. These emotions are:
- Interest
- Joy
- Surprise
- Sadness
- Anger
- Disgust
- Contempt
- Fear
- Shame
- Guilt
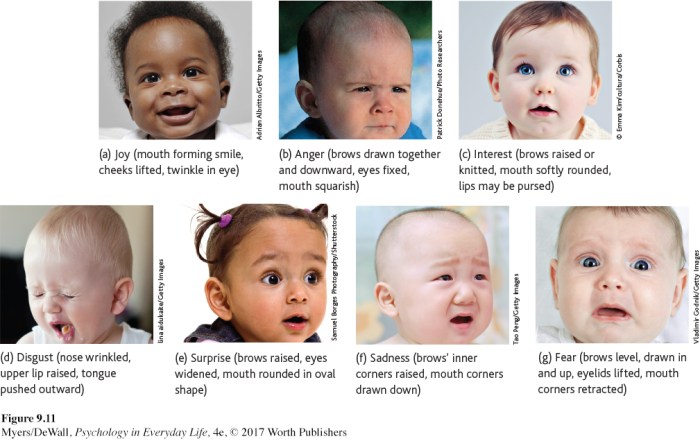
Each of these emotions is associated with a specific facial expression. For example, interest is expressed by raising the eyebrows and widening the eyes, while joy is expressed by smiling and laughing.
Examples of Emotional Expressions
The following are some examples of how emotions are expressed through facial expressions:
- A person who is interested in something will raise their eyebrows and widen their eyes.
- A person who is happy will smile and laugh.
- A person who is surprised will raise their eyebrows and open their mouth.
- A person who is sad will have a downcast expression and may cry.
- A person who is angry will have a furrowed brow and clenched teeth.
Izard’s theory of emotion has been influential in the field of psychology and has helped to increase our understanding of the relationship between emotions and facial expressions.
Izard’s Research on Love
Carroll Izard’s research on love has shown that it is a complex emotion that is expressed in a variety of ways. He identified ten basic emotions, including love, and believed that these emotions are innate and universal. Izard’s research has also shown that love plays an important role in human development, helping us to form relationships and connect with others.
Expressions of Love
Izard’s research has shown that love can be expressed in a variety of ways, both verbally and nonverbally. Some of the most common ways that love is expressed include:
- Physical affection, such as hugging, kissing, and holding hands
- Verbal expressions, such as saying “I love you” or “I care about you”
- Acts of service, such as doing things for someone else without expecting anything in return
- Spending time together
- Sharing experiences
The Role of Love in Human Development
Love plays an important role in human development, helping us to form relationships and connect with others. It is essential for our emotional and social well-being. Love helps us to feel secure, valued, and loved. It also helps us to learn how to trust and cooperate with others.
Research has shown that children who grow up in loving homes are more likely to be successful in school, have healthy relationships, and be happy and well-adjusted adults.
Izard’s Theory and Love Relationships: Carroll Izard Says That Love
Carroll Izard’s theory of emotion provides a framework for understanding the emotions involved in love relationships. According to Izard, there are ten basic emotions: interest, joy, surprise, sadness, anger, disgust, contempt, fear, shame, and guilt. These emotions can be combined to create a wide range of more complex emotions, such as love.
In love relationships, the most common emotions are:
Intimacy and Love
- Intimacy:A feeling of closeness and connection with another person.
- Love:A strong feeling of affection and attachment for another person.
- Trust:A belief that another person is reliable and trustworthy.
- Commitment:A willingness to stay in a relationship even through difficult times.
Positive Emotions
- Joy:A feeling of happiness and contentment.
- Surprise:A feeling of astonishment or wonder.
- Interest:A feeling of curiosity or excitement.
Negative Emotions, Carroll izard says that love
- Sadness:A feeling of unhappiness or sorrow.
- Anger:A feeling of hostility or resentment.
- Disgust:A feeling of revulsion or distaste.
- Contempt:A feeling of disdain or scorn.
- Fear:A feeling of anxiety or apprehension.
- Shame:A feeling of guilt or embarrassment.
- Guilt:A feeling of remorse or regret.
These emotions can be expressed in a variety of ways, both verbally and nonverbally. For example, intimacy can be expressed through physical touch, eye contact, and sharing personal thoughts and feelings. Love can be expressed through words of affection, gifts, and acts of service.
Trust can be expressed through keeping promises and being reliable. Commitment can be expressed through staying in a relationship even through difficult times.
Carroll Izard suggests that love is a complex emotion involving multiple components. The American Counseling Association (ACA) has established a code of ethics for 2024 that outlines ethical principles for counselors, including the importance of maintaining healthy relationships with clients.
This code can help counselors navigate the complexities of love and relationships in a professional and ethical manner, ensuring that clients receive the best possible care.
Izard’s Theory and Emotional Intelligence

Emotional intelligence (EI) refers to an individual’s ability to understand, manage, and use their own emotions and the emotions of others. Carroll Izard’s theory of emotion provides a framework for understanding the role of emotions in EI.
According to Izard, emotions are discrete, innate responses that are triggered by specific stimuli. He identified ten basic emotions: joy, interest, surprise, sadness, anger, disgust, contempt, fear, shame, and guilt. These emotions are expressed through facial expressions, physiological changes, and subjective experiences.
Developing Emotional Intelligence
Izard’s theory suggests that EI can be developed by enhancing one’s ability to:
- Identify and label emotions:Accurately recognizing and naming emotions in oneself and others is crucial for understanding and managing them.
- Regulate emotions:Managing emotions involves controlling their intensity, duration, and expression. This includes strategies such as self-soothing, problem-solving, and seeking support.
- Use emotions effectively:Emotions can be harnessed for positive outcomes. For example, anger can motivate action, while joy can foster creativity.
Improving Emotional Intelligence
EI can be improved through various methods, including:
- Self-reflection:Paying attention to one’s own emotions and how they impact thoughts and behaviors.
- Feedback from others:Seeking constructive criticism and perspectives from trusted individuals.
- Emotional skills training:Participating in workshops or programs designed to enhance EI.
Examples of Emotional Intelligence in Everyday Life
- Empathy:Understanding and responding to the emotions of others.
- Conflict resolution:Managing emotions during disagreements and finding mutually acceptable solutions.
- Decision-making:Considering the emotional impact of decisions and making choices that align with one’s values.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key principles of Izard’s theory of emotion?
Izard’s theory emphasizes the innate nature of emotions, their distinct physiological expressions, and their role in adaptive behavior.
How does Izard define love?
Izard describes love as a complex emotion involving care, protectiveness, and joy, which is often accompanied by physiological arousal.
What are the different ways that love is expressed?
Love can be expressed through physical touch, affectionate words, acts of kindness, and shared experiences.


