Embark on a captivating journey with the phlebotomy order of draw quiz! This interactive exploration unveils the crucial importance of maintaining a standardized blood collection sequence. Delve into the nuances of the CLSI order of draw, understanding the rationale behind each tube type’s placement.
Unravel the secrets of blood collection tubes and additives, discovering their specific purposes and functions. Explore the potential pitfalls that can arise when the order of draw is compromised, including hemolysis, contamination, and clotting. Learn how to navigate special considerations for specific patient populations and ensure the integrity of blood specimens.
Phlebotomy Order of Draw Basics
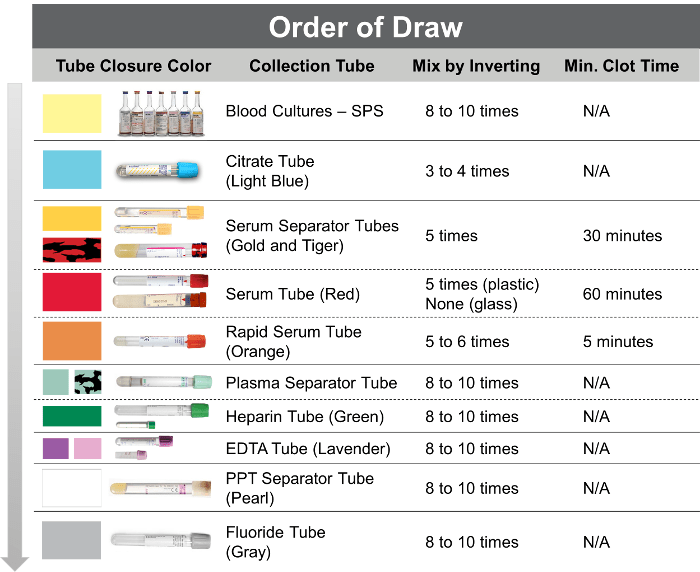
Maintaining a standard order of draw is crucial in blood collection to ensure the integrity of the sample and accurate test results. The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) has established a specific order of draw to minimize contamination and interference among different additives and analytes.
CLSI Order of Draw
The CLSI order of draw is as follows:
- Blood culture tubes: Collected first to avoid contamination from other tubes.
- Light blue top (citrate): Used for coagulation studies, such as prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT).
- Red top (no additive): Used for serum tests, such as chemistry panels and immunoassays.
- Lavender top (EDTA): Used for hematology tests, such as complete blood count (CBC) and differential.
- Green top (heparin): Used for plasma tests, such as glucose and electrolytes.
- Gray top (sodium fluoride): Used for glucose tests, as fluoride inhibits glycolysis.
The sequence of tube types is based on the following rationale:
- Blood culture tubes must be collected first to avoid contamination.
- Citrate tubes are collected next to prevent coagulation, which can interfere with serum tests.
- Red top tubes are collected for serum tests, as they do not contain additives that can interfere with the analysis.
- EDTA tubes are collected for hematology tests, as EDTA prevents platelet aggregation and preserves the integrity of white blood cells.
- Heparin tubes are collected for plasma tests, as heparin prevents coagulation without affecting the concentration of analytes in plasma.
- Sodium fluoride tubes are collected last, as fluoride inhibits glycolysis and preserves glucose levels.
Tube Types and Additives
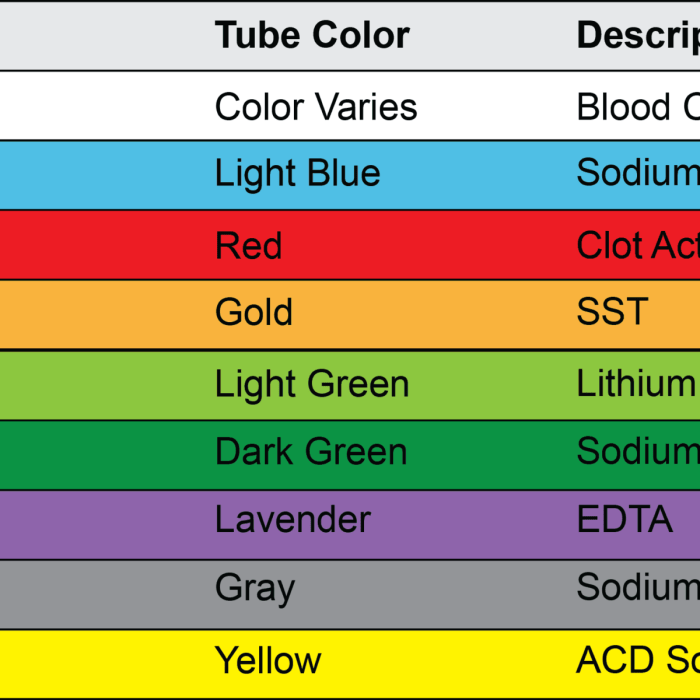
In phlebotomy, various types of blood collection tubes are used, each containing specific additives to preserve the integrity and stability of the blood sample for different tests. Understanding the purpose and function of these additives is crucial for accurate and reliable laboratory results.
Tube Types and Additives
| Tube Type | Color | Additive | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum Tube | Red | None | Allows clot formation and serum separation for biochemical tests |
| Plasma Tube | Green | Sodium Citrate | Anticoagulant that prevents blood from clotting for coagulation studies |
| Heparin Tube | Green (light) | Heparin | Anticoagulant that prevents blood from clotting for hematology tests |
| EDTA Tube | Lavender | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) | Anticoagulant that prevents blood from clotting and preserves cell morphology for hematology tests |
| Glycolysis Inhibitor Tube | Gray | Sodium Fluoride and Potassium Oxalate | Preserves glucose levels by inhibiting glycolysis for glucose testing |
Potential Interferences: Phlebotomy Order Of Draw Quiz
Incorrect order of draw can lead to potential interferences that can affect the accuracy of blood test results. These interferences include hemolysis, contamination, and clotting.
Hemolysis
Hemolysis occurs when red blood cells are ruptured, releasing hemoglobin into the plasma. This can interfere with tests that measure analytes in the plasma, such as electrolytes, glucose, and creatinine. Hemolysis can be caused by several factors, including using the wrong needle gauge, applying too much pressure when drawing blood, or drawing blood too quickly.
Contamination
Contamination can occur when blood from one tube enters another tube. This can happen if the tubes are not properly capped or if the blood is not drawn in the correct order. Contamination can interfere with tests that measure analytes in the plasma or serum, such as blood counts, coagulation studies, and chemistry panels.
Clotting
Clotting can occur when blood is exposed to air. This can happen if the blood is not drawn into the tube properly or if the tube is not capped immediately after the blood is drawn. Clotting can interfere with tests that measure analytes in the plasma or serum, such as coagulation studies and chemistry panels.
Special Considerations
Certain patient populations require special considerations during blood collection to ensure accurate results and minimize discomfort.
For patients receiving anticoagulant therapy, such as warfarin or heparin, the order of draw must be modified to avoid contamination of the blood sample with anticoagulant. In such cases, blood for coagulation studies should be drawn first, followed by blood for other tests.
For those prepping for a phlebotomy order of draw quiz, the process can seem daunting. However, with practice and understanding, you’ll master it. On a lighter note, have you heard about the obituary for Romeo and Juliet ? It’s quite a tragic tale, but it’s also a reminder that even in the face of adversity, we must keep our focus.
Back to phlebotomy, remember the order of draw: blood culture, light blue, red, green, and lavender. Stay sharp, and you’ll ace that quiz!
Patients with Compromised Veins
Patients with compromised veins may require special techniques to obtain a blood sample. These techniques include using a smaller gauge needle, applying a warm compress to the venipuncture site, or using a butterfly needle.
Handling and Transporting Blood Specimens
Proper handling and transportation of blood specimens are crucial to ensure the integrity of the samples. Blood specimens should be:
- Labeled with the patient’s name, date of collection, and time of collection.
- Stored at the appropriate temperature (e.g., refrigerated or on ice) as per the specific test requirements.
- Transported to the laboratory promptly and in a manner that minimizes agitation or damage to the specimens.
Quality Control and Best Practices
Ensuring the accuracy of phlebotomy procedures is paramount, and various quality control measures are implemented to safeguard the integrity of blood samples.
Standardized Protocols and Guidelines
Adhering to standardized protocols and guidelines is crucial in phlebotomy. These protocols Artikel proper techniques for blood collection, handling, and processing, ensuring consistency and minimizing errors.
Quality Control Checks
Regular quality control checks are conducted to monitor the accuracy of phlebotomy procedures. These checks may include:
- Verifying equipment calibration
- Assessing staff competency
- Reviewing patient identification and sample labeling
li>Evaluating blood collection volumes and sample integrity
Best Practices for Proper Technique, Phlebotomy order of draw quiz
Maintaining proper technique during blood collection is essential to minimize errors and ensure sample quality. Best practices include:
- Using the appropriate needle size and vacuum pressure
- Positioning the patient comfortably and stabilizing the puncture site
- Drawing blood smoothly and avoiding excessive force
- Mixing samples thoroughly to prevent clotting
Minimizing Errors
By implementing quality control measures and adhering to best practices, phlebotomists can minimize errors during blood collection. Common errors to avoid include:
- Incorrect patient identification
- Improper sample handling
- Insufficient blood volume
- Hemolysis or contamination
Following standardized protocols, conducting quality control checks, and maintaining proper technique are essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of phlebotomy procedures.
FAQ Corner
What is the significance of maintaining a standard order of draw?
Preserving the order of draw minimizes the risk of contamination and ensures the accuracy of blood test results.
How does hemolysis affect blood test results?
Hemolysis, the rupturing of red blood cells, can interfere with the analysis of certain analytes, leading to inaccurate results.
What special considerations should be taken for patients receiving anticoagulant therapy?
For patients on anticoagulants, the order of draw may need to be modified to prevent the contamination of subsequent tubes.