Kayla swift was diagnosed with infectious mononucleosis. – Kayla Swift’s recent diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis, commonly known as mono, has raised awareness about this prevalent viral infection. Mono is characterized by a constellation of symptoms, including fatigue, fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. Understanding the nature of mono, its transmission, and available treatment options is crucial for both healthcare professionals and the general public.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of infectious mononucleosis, providing valuable insights into its diagnosis, complications, and preventive measures.
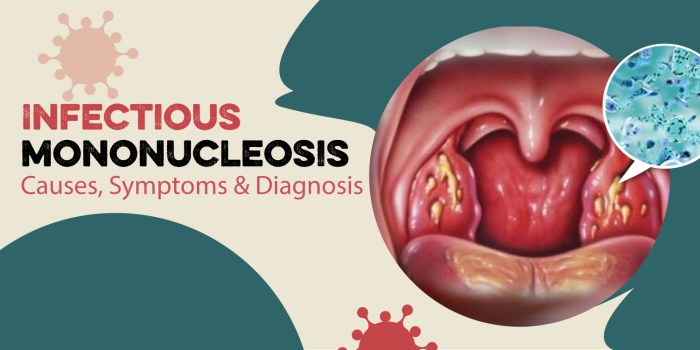
Infectious Mononucleosis (Mono)
Infectious mononucleosis, commonly known as mono, is a contagious disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). It primarily affects adolescents and young adults and is characterized by a triad of symptoms: fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes.
EBV is spread through contact with infected saliva, typically through kissing or sharing drinks or utensils. The virus enters the body through the mouth and throat and replicates in the lymphoid tissue, leading to the characteristic symptoms of mono.
Complications of Infectious Mononucleosis, Kayla swift was diagnosed with infectious mononucleosis.
While most cases of mono are self-limiting and resolve within a few weeks, some individuals may experience complications. These include:
- Enlarged spleen
- Liver inflammation
- Neurological complications, such as encephalitis and Guillain-Barré syndrome
- Myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle)
- Rupture of the spleen (rare)
Diagnosis of Infectious Mononucleosis: Kayla Swift Was Diagnosed With Infectious Mononucleosis.
Diagnosis of mono is based on a combination of clinical symptoms and laboratory tests. A physical examination may reveal swollen lymph nodes, particularly in the neck and armpits, as well as a characteristic “beefy red” throat.
Blood tests are essential for confirming the diagnosis. These tests include:
- Complete blood count (CBC): Shows elevated white blood cell count, particularly atypical lymphocytes
- Heterophile antibody test: Detects antibodies against heterophile antigens, which are produced in response to EBV infection
- Epstein-Barr virus-specific antibody tests: Confirms the presence of EBV-specific antibodies
Treatment of Infectious Mononucleosis
There is no specific cure for mono. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and supporting the immune system. Rest and supportive care are crucial:
- Get plenty of rest
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- Avoid strenuous activity
In some cases, antiviral medications may be prescribed to reduce the severity of symptoms and prevent complications. These medications include:
- Acyclovir
- Valacyclovir
- Famciclovir
Prevention of Infectious Mononucleosis
There is no vaccine available for infectious mononucleosis. Prevention focuses on reducing the risk of exposure to the virus:
- Avoid kissing or sharing drinks or utensils with someone who has mono
- Practice good hygiene, including frequent hand washing
- Avoid contact with anyone who has a fever or sore throat
Top FAQs
What is the primary mode of transmission for infectious mononucleosis?
Infectious mononucleosis is primarily transmitted through contact with infected saliva, commonly known as the “kissing disease.”
What are the potential complications associated with infectious mononucleosis?
Complications of mono can include splenomegaly, hepatitis, encephalitis, and myocarditis, although these are relatively rare.
Is there a vaccine available to prevent infectious mononucleosis?
Currently, there is no widely available vaccine for infectious mononucleosis.