Embark on an educational journey with “A Very Big Branch iCivics Answer Key,” an indispensable resource for deciphering the intricacies of the U.S. government. This comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, providing a profound understanding of their roles, responsibilities, and interactions.
Delve into the structural foundations of the U.S. Congress, unraveling the dynamics of the Senate and House of Representatives. Explore the vast powers vested in the President and delve into the intricate workings of the Cabinet and other executive agencies.
Uncover the enigmatic functions of the Supreme Court and other federal courts, gaining insights into the interpretation and application of laws.
Branch Terminology
In the context of government, a branch refers to a division or department within the governing body that exercises specific powers and responsibilities. Different types of branches exist within a government system, each with its own unique role and function.
Types of Branches
Common types of branches in a government system include:
- Legislative Branch:Responsible for making laws and policies.
- Executive Branch:Responsible for implementing and enforcing laws.
- Judicial Branch:Responsible for interpreting and applying laws.
Separation of Powers
The separation of powers is a fundamental principle in many government systems. It involves dividing the powers of government among different branches to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful. This separation ensures checks and balances, where each branch has the ability to limit or control the actions of the others.
Branches of the U.S. Government: A Very Big Branch Icivics Answer Key
The United States government is a system of checks and balances, with three separate but coequal branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. Each branch has its own powers and responsibilities, and each can check the power of the other two branches.
The legislative branch is responsible for making laws. It is composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Senate has 100 members, two from each state. The House of Representatives has 435 members, who are elected from districts based on population.
The legislative branch also has the power to declare war, raise taxes, and approve treaties.
The executive branch is responsible for carrying out the laws. It is headed by the President, who is elected by the people. The President also appoints the heads of the various executive departments, such as the Department of State, the Department of Defense, and the Department of Justice.
The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting the laws. It is composed of the Supreme Court, which has nine justices, and the lower federal courts. The Supreme Court has the power to declare laws unconstitutional.
Checks and Balances
The system of checks and balances is designed to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. For example, the legislative branch can pass laws, but the executive branch can veto them. The judicial branch can declare laws unconstitutional, but the legislative branch can override those decisions with a two-thirds vote.
The system of checks and balances is a fundamental part of the American government. It helps to ensure that the government is responsive to the needs of the people and that no one branch can become too powerful.
Structure of the Legislative Branch
The Legislative Branch of the U.S. government is responsible for making laws. It consists of the U.S. Congress, which is made up of the Senate and the House of Representatives.The Senate is composed of 100 members, two from each state.
Senators serve six-year terms, and one-third of the Senate is up for election every two years. The Vice President of the United States serves as the President of the Senate, but only votes in the case of a tie.The House of Representatives is composed of 435 members, who are elected from districts within each state.
The number of representatives each state gets is based on its population. Representatives serve two-year terms, and the entire House is up for election every two years. The Speaker of the House is the presiding officer of the House of Representatives.The
process of passing legislation begins when a bill is introduced in either the House or the Senate. The bill is then referred to a committee, which studies the bill and makes recommendations. The committee can approve the bill, reject it, or amend it.If
the committee approves the bill, it is then sent to the full House or Senate for a vote. If the bill passes, it is then sent to the other chamber for consideration. If the other chamber also passes the bill, it is then sent to the President for his signature.
If the President signs the bill, it becomes law.
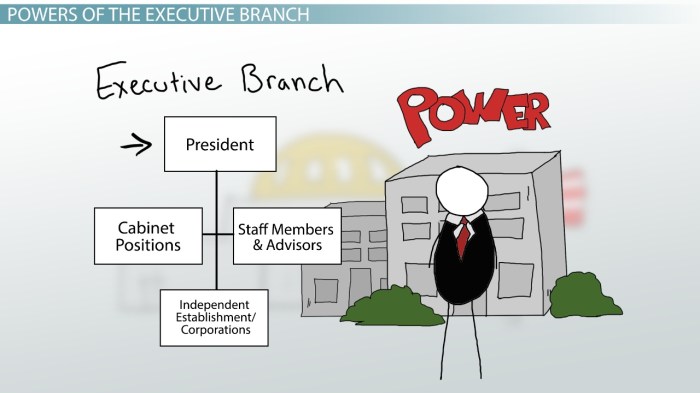
Powers of the Executive Branch

The executive branch of the U.S. government is headed by the President, who is responsible for enforcing laws and implementing policies. The President has a wide range of powers, including the power to veto legislation, appoint judges and other officials, and command the armed forces.The
President is assisted by a Cabinet of advisors, each of whom heads a different executive department. The Cabinet includes the Secretary of State, Secretary of the Treasury, Secretary of Defense, and Attorney General.Other executive agencies include the Environmental Protection Agency, the Food and Drug Administration, and the Federal Trade Commission.
These agencies are responsible for regulating various aspects of American life, from environmental protection to consumer safety.
Enforcing Laws and Implementing Policies
The executive branch is responsible for enforcing laws and implementing policies. The President has the power to issue executive orders, which have the force of law. The President can also use the military to enforce laws and protect the country.The
executive branch also works with Congress to implement policies. The President can propose legislation to Congress, and the President can sign or veto bills passed by Congress.
Functions of the Judicial Branch

The judicial branch of the U.S. government is responsible for interpreting and applying the laws of the land. It is composed of the Supreme Court, the federal courts of appeals, and the federal district courts. The Supreme Court is the highest court in the land and has the final say on all matters of law.
The federal courts of appeals are responsible for reviewing decisions made by the federal district courts. The federal district courts are responsible for hearing cases involving federal law.
Role of the Supreme Court
The Supreme Court has the power to interpret the Constitution and to strike down laws that it finds to be unconstitutional. It also has the power to review decisions made by the lower federal courts.
The Supreme Court is composed of nine justices who are appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate. The justices serve for life, which gives them a great deal of independence from the other branches of government.
Process of Interpreting and Applying Laws
When a court interprets a law, it must first determine the meaning of the words used in the law. The court will then apply the law to the facts of the case before it.
Courts often have to interpret laws that are ambiguous or that have multiple possible meanings. In these cases, the court will use a variety of factors to determine the meaning of the law, including the text of the law, the legislative history of the law, and the precedents set by other courts.
Importance of Judicial Independence
Judicial independence is essential to the proper functioning of the judicial branch. Without judicial independence, the courts would be subject to political pressure and would not be able to make impartial decisions.
There are a number of factors that contribute to judicial independence, including the lifetime appointments of Supreme Court justices, the fact that judges cannot be removed from office except through impeachment, and the tradition of judicial restraint.
Interbranch Cooperation and Conflict
The three branches of the U.S. government—legislative, executive, and judicial—are designed to work together to ensure that the government is responsive to the needs of the people and that no one branch becomes too powerful.
However, there are times when the branches cooperate and times when they conflict. These interactions are essential to the functioning of the government and the preservation of the system of checks and balances.
Examples of Cooperation, A very big branch icivics answer key
There are many examples of cooperation between the branches of government. For instance, the president and Congress work together to pass laws. The president proposes legislation, and Congress debates and votes on it. If a bill passes both chambers of Congress, it is sent to the president for his signature.
If the president signs the bill, it becomes law.
Another example of cooperation is the relationship between the Supreme Court and the other branches of government. The Supreme Court has the power to interpret laws and declare them unconstitutional. This power helps to ensure that the other branches of government do not overstep their authority.
Instances of Conflict
There are also times when the branches of government conflict. For example, the president and Congress may disagree on a particular policy. In such cases, the president may veto a bill passed by Congress, or Congress may override a presidential veto.
Another example of conflict is the relationship between the Supreme Court and the other branches of government. The Supreme Court has the power to declare laws unconstitutional, which can lead to conflict with the other branches of government.
Role of the Media and Public Opinion
The media and public opinion play an important role in interbranch relations. The media can inform the public about the actions of the different branches of government and can hold them accountable for their actions. Public opinion can also influence the actions of the different branches of government.
For example, if the public is strongly opposed to a particular policy, it may put pressure on the president or Congress to change their position.
FAQ Corner
What is the primary function of the legislative branch?
To make laws and oversee the executive branch.
What is the role of the President in the executive branch?
To enforce laws, conduct foreign policy, and serve as commander-in-chief of the armed forces.
How does the judicial branch interpret laws?
By applying legal principles to specific cases and controversies.